Payroll software automates the process of paying salaried, hourly and contingent employees. Vendors of human resources (HR) technology and specialized payroll companies often sell payroll software as standalone products.
Payroll software is increasingly a central component of integrated, multifunctional human capital management (HCM) systems. Compared with paper-based systems, payroll software speeds up the online payroll process while reducing errors and enabling managers to more easily customize paychecks for individual employees.
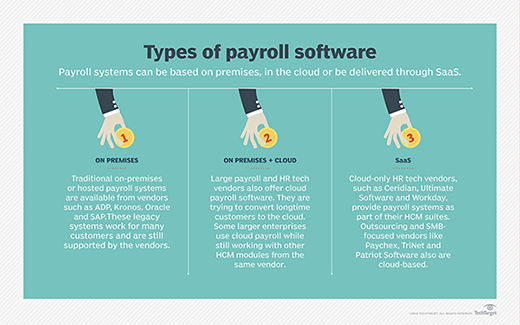
This software is often delivered on premises, both on premises and in the cloud, or through software as a service. It is considered part of core HR software.
How does payroll software work?
Payroll software integrates various business systems, such as accounting software, as well as employee attendance and time tracking, and human resource management software. Employee information, including salary details, benefits information, tax withholdings and deductions, is securely stored in the system. When it’s time to run payroll, the software accesses this information and calculates the appropriate wages, tax payments and deductions based on predefined local, state and national tax rules and tax compliance regulations. It also produces payroll statements and automated payroll reports.
Payroll software streamlines processes that generate pay stubs, facilitates direct deposits to employees’ bank accounts and physical check printing, and makes tax payments with the appropriate government agencies, such as the Internal Revenue Service. Many payroll systems offer self-service portals where employees can access their pay stubs, update personal information, and manage paid time off (PTO) requests and calendars.
Payroll software features
Most payroll software products share similar sets of features:
- Automation and full-service payroll. Payroll software offers several business process automation features, including automatic calculation of deductions for withholdings, such as taxes, insurance and retirement contributions, and any other additional fees. Payroll software also commonly processes direct paycheck deposits, generates tax forms and deducts wage garnishments. Payroll administrators can configure systems to print checks for employees not enrolled in direct deposit. Many payroll providers also offer unlimited payroll runs.
- Self-service. Many payroll systems include employee self-service capabilities that let employees view and download payroll statements online from mobile devices and computers. Self-service systems also provide intuitive functionality so that employees can make changes to deductions, withholding amounts, health insurance and other benefits, and other payroll features.
- Customization. Some payroll software systems let HR administrators and IT staff configure them to accommodate the needs of both large and small businesses. Customizable features enable admins to adjust accumulations, balance periods and pay groups.
- Reporting and analytics. Other payroll management features include setting gross-to-net income and running payroll balance and calculation reports. Some business payroll systems work with payroll data analytics modules that can create customized audit reports and track local, national and global payroll spending trends in real time.
- Payroll tax filing. Payroll software automatically files and pays payroll taxes to the appropriate government agencies, ensuring compliance with national and local tax laws and regulations.
- Scalability. Payroll software is designed to be scalable. This means it can accommodate growing businesses, integrating new employees, additional pay structures and expanded compliance requirements.
Benefits of using payroll software
Organizations of all sizes use payroll software, often integrated with the core HR system, for benefits such as the following:
- Increased efficiency through automation, enabling organizations to focus on core operations and save on costs.
- User-friendly self-service portals.
- Customer support, including onboarding new hires, assisting in software integration and offering answers to frequently asked questions.
- Flexible pricing plans, tailoring payroll needs to specific organizations.
- Cloud-based and mobile accessibility, enabling companies to store information in the cloud and access it through the mobile app.
- Assistance with legal and tax regulatory compliance.

Does payroll software help with regulatory compliance?
Regulatory compliance is a key benefit of payroll software, which is designed to stay up to date with constantly evolving labor laws, such as workers’ compensation laws at the federal, state and local levels. By automating tax calculations, filings and payments, payroll software helps ensure that businesses remain compliant with all applicable rules and regulations.
Furthermore, payroll software often includes features such as electronic storage of employee records, generating mandatory forms such as W-2s and W-9s, and tracking employee hours worked and PTO. Many providers offer compliance support, with access to knowledgeable professionals who can assist in navigating complex regulatory compliance and tax calculation.
Country-specific payroll software
The largest payroll software vendors provide customized systems for the U.S. and other countries using local currency. They are able to process different countries’ taxes and track compliance obligations.
ADP offers HCM systems with integrated payroll services in more than 140 countries, according to the company, and it’s considered a leading multicountry payroll software company, according to a 2023 Gartner report. Dayforce, formerly Ceridian HCM, offers payroll software for more than 200 countries and territories. Other vendors with multicountry payroll capabilities include Cegid, Oracle, SAP, UKG and Workday.
Payroll software is an important HR software tool. Learn about the top HR software tools available.

