Salesforce Platform (formerly known as Force.com) is a platform as a service (PaaS) product that simplifies the development and deployment of cloud-based applications and websites. Using Salesforce Platform, developers can create many kinds of enterprise and business applications without using additional hardware or software or worrying about database maintenance.
Overview of Salesforce Platform
Launched in 2007, Force.com was a PaaS offering from Salesforce. It was one of the world’s first PaaS products and the first to facilitate turnkey multi-tenancy for internet-scale applications. This custom application development environment now provides a user-friendly, low-code way to build apps and automations that can help to boost enterprise efficiency and productivity and potentially reduce IT costs.
Salesforce Platform enables developers to create almost any application at any scale. In fact, other Salesforce software-as-a-service applications, such as Marketing Cloud or Sales Cloud, are built upon it.
Salesforce Platform offers a low-code approach to application development. End users can create simple business apps to meet their needs with reusable code segments. The AppExchange marketplace contains thousands of prebuilt apps that can be immediately deployed. It even incorporates Einstein 1, enabling easy artificial intelligence (AI) integration.
Developers can use Salesforce Platform’s cloud integrated development environment and point-and-click tools to create the required apps and websites. They can then deploy the apps and sites to Salesforce Platform’s multi-tenant servers so end users can start using them quickly.
Advanced developers can use the entire Salesforce Developer Experience software development toolkit to code and deploy an app. Salesforce DX enables Salesforce Platform apps to follow Agile development principles and use continuous integration/continuous delivery deployment practices, while using tools familiar to most developers.
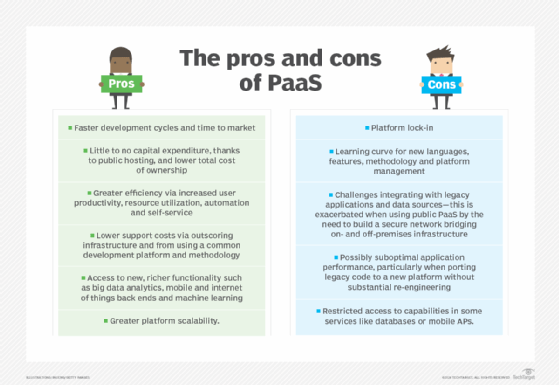
Salesforce Platform and platform as a service
PaaS refers to a cloud-based environment for developing and deploying enterprise applications. The PaaS provider provides all the necessary development resources, including hardware infrastructure, middleware, development tools, business intelligence services and database management systems.
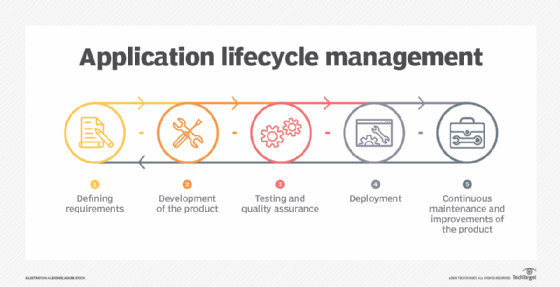
A PaaS like Salesforce Platform supports the entire application lifecycle management process — from build, test and deploy to post-deployment tasks, such as maintenance and updates. Salesforce Platform also abstracts the concept of servers, so developers don’t have to worry about server-related tasks, like configuration or management.
In addition, the PaaS provider takes care of other infrastructure-related concerns, like application availability, load balancing, data backups, operating system patch management and security. As a result, developers can focus on application development and customization. And, when the application is ready to be deployed, it can be done easily, often with just a few clicks.
Multi-tenancy architecture of Salesforce Platform
Salesforce Platform features an optimized and patented metadata-driven architecture for creating scalable, high-performance and customizable applications. Moreover, the architecture is multi-tenant, meaning it can meet the needs of multiple companies or departments using the same set of resources. This concept makes Salesforce Platform different from single-tenant products, where a dedicated set of resources are required to satisfy the needs of each specific organization.
The multi-tenancy architectural approach enables Salesforce, Salesforce Platform’s provider, to achieve economies of scale because it can serve multiple organizations using a common set of resources and a single codebase. In addition, it needs to manage only one software stack and one set of hardware, which reduces the Salesforce Platform maintenance burden.
The approach also creates advantages for organizations using the service. They can customize their Salesforce Platform instance per their unique requirements. At the same time, all their data and customizations remain secure because they are insulated from all other Salesforce Platform tenants. They can also benefit from improved quality, lower costs and frequent improvements to the platform, which are possible because multi-tenancy enables the provider to save on its own development and maintenance costs.
Finally, multi-tenancy enables the customer organization to run all its applications in one space. As a result, any authorized user of any application can access specific data sets, which then makes it easy to integrate related applications and their data. Users don’t need to worry about which geographic region their data is stored in or how to access one resource from another.
The importance of metadata in Salesforce Platform
Salesforce Platform’s metadata-driven architecture is stable, scalable and reliable. In this context, metadata refers to internal representations of everything exposed to application developers and users using Salesforce Platform, such as the following:
- Tenant-specific customizations.
- Business logic.
- Definitions of underlying data tables and indexes.
- User access privileges.
- Workflows.
- Flows and reports.
All these abstract constructs exist as metadata in Salesforce Platform’s Universal Data Dictionary. This metadata is stored in the platform’s engine, which then generates virtual application components at runtime. It thus enables the development of high-performance, highly customizable, multi-tenant, on-demand applications. Moreover, it’s easy to modify or customize applications; all that’s needed is a simple nonblocking update to the corresponding metadata.
In Salesforce Platform’s architecture, application components are different from metadata, which is different from application data. Some metadata describes an application’s base functionality, while other metadata describes each tenant’s data and customizations. These different data types are clearly separated, which enables independent updates to the system kernel and risk-free modifications to the core application.
Further, the platform prevents performance sapping disk input/output and code recompilations and improves application response times by using metadata caches. These caches maintain the most recently used metadata in memory, thus optimizing metadata access and enabling the platform to scale.
Common uses of Salesforce Platform
Salesforce Platform is useful for building many types of enterprise applications and workflows. One example is a business process automation (BPA) app to automate repetitive or predictable processes to save time, reduce errors and produce more consistent output.
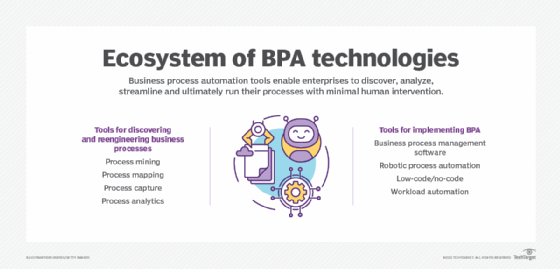
The platform is also ideal for building intelligent workflows, predictive sales dashboards and smart service workflows, all achievable with writing little or no code. These apps can run on any device, including mobile devices, so developers don’t have to create separate codebases or use different development tools.
Salesforce Platform also includes capabilities to help enterprises do the following:
- Integrate, analyze, mine and extend customer relationship management (CRM) data.
- Build customer apps.
- Build employee apps.
- Design and deliver personalized customer experiences.
- Improve business forecasting.
- Inform product design decisions.
Benefits of Salesforce Platform
Salesforce Platform provides a comprehensive ecosystem of tools and services for building, running, managing and optimizing a vast range of enterprise apps. This ecosystem includes the following:
- User interface (UI) frameworks and components to speed up development.
- A mobile software development kit to build native apps for iOS and Android.
- Multilanguage support.
- Social collaboration tools.
- Cloud identity solutions.
- Page layouts.
- 1-to-1 customer engagement engine.
- Custom actions.
Developers can use these tools to build the apps without having to worry about activities related to infrastructure setup, database management, server management, security, etc.
The platform is API-first, so it’s easy to build any kind of app with any desired UI. All apps connect to business data, enabling a more connected tech ecosystem and better business decision-making. Also, the platform enables both instant app deployment and real-time app distribution.
Business users also benefit from Salesforce Platform. They can easily translate their business ideas into applications. The apps can be social and mobile-friendly, as well as contextually aware and action-oriented. They can also easily add new users, control user access and deliver useful insights to other business users.
Salesforce maintains the security of the system. Organizations can spend less time hardening application security and keeping software up to date. The built-in security and identity services can help prevent data breaches and keep data access controls compliant.
Follow these steps to ensure a smooth and eventless CRM adoption process. Also, learn about the history and evolution, benefits and challenges, and types of CRM systems. See ways CRM improves customer experience and steps for negotiating deals with Salesforce. Compare AI-powered CRM platforms and top customer data platform software products.
