SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) is a component of SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that helps businesses support and maintain equipment and systems. With this module, organizations can streamline and control maintenance activities for their plants and machines to ensure that they operate optimally.
Modern plants are prone to numerous challenges that can result in machinery downtime or operational disruptions. To prevent such issues, plant managers must ensure that all equipment is regularly monitored and properly maintained. However, monitoring and maintenance can be a complicated endeavor that depends on various factors, such as plant size and machinery type.
SAP PM helps to minimize the complexity. With SAP PM, users — most often maintenance and operations managers — can monitor their plants and equipment. They can also plan and execute maintenance activities. By streamlining maintenance, SAP PM helps to optimize system and plant performance and prevent costly breakdowns or malfunctions.
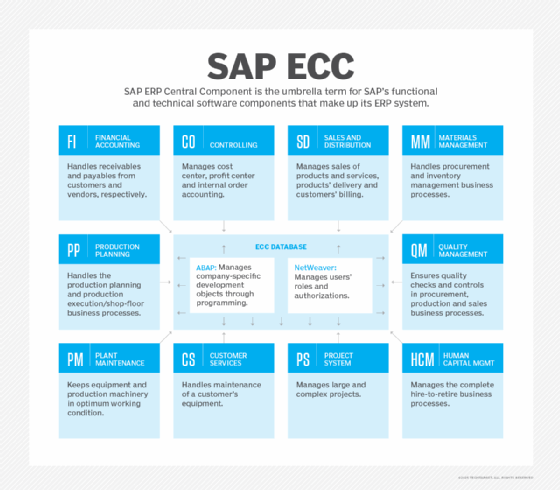
SAP PM is included in SAP ECC, the base layer of SAP Business Suite, which provides a holistic view of business operations to facilitate data-driven decision-making. SAP ECC includes numerous components apart from SAP PM, such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM) and Financial Accounting (FI).
What is SAP PM used for?
Plant managers, maintenance teams and other users in industrial settings can use SAP PM to easily manage and execute maintenance requests for plants or equipment. Prior to execution, users can inspect the condition of the asset to determine what, if any, maintenance activities it requires.
SAP PM also makes it easy to do the following:
- Capture tangible data about equipment use and wear and tear.
- Identify required repairs and perform automatic repairs.
- Document issues and costs.
- Streamline asset management.
- Plan labor- and material-related activities.
- Execute orders to purchase nonstock spare parts and maintenance services.
Functions of SAP PM
SAP PM performs three main functions to help industrial companies maintain their plants, technical systems and equipment. Each function can include multiple measures to achieve its main objective. These functions are the following:
- Inspection helps determine the condition of the systems or equipment. The results of an inspection aid in preventive maintenance and highlight areas where malfunctions or downtime are imminent.
- Preventive maintenance helps to maintain ideal conditions for the system or equipment, thus ensuring high availability and optimal performance.
- Repair restores the systems or equipment to ideal condition, whether that be by conducting repairs, replacing parts or creating purchase requisitions.
Apart from inspection, preventive maintenance and repair, the maintenance organization might also implement other measures using SAP PM to perform, streamline and optimize maintenance activities and maximize plant and equipment uptime.
Key benefits of SAP PM
SAP PM enables proactive and regular plant and equipment monitoring and maintenance. It provides solid data that enables plant personnel to identify potential problems and act quickly to prevent them. It helps to reduce downtime and maximize system availability and service life. Since regular maintenance keeps equipment in good working condition, it minimizes and delays expensive replacements and can lead to active cost savings that way.
SAP PM also centralizes all maintenance-related tasks. This simplifies equipment monitoring, provides greater control over activities, and increases transparency and accountability throughout the plant.
Who uses SAP PM?
There are four groups of users that benefit most from SAP PM:
- Maintenance and operations managers use PM to obtain metrics on equipment performance, maintenance requests or deployments. PM improves maintenance-related decision-making by generating useful reports about planned, in-process or completed work. SAP PM also provides accurate and up-to-date data about a system’s maintenance history and relative maintenance costs, enabling maintenance and operations managers to effectively plan and budget for equipment repairs, replenishments or upgrades.
- Production line workers and equipment users can use PM to manage maintenance issues more promptly and effectively. For example, they can coordinate preventive maintenance issues with managers and maintenance personnel to ensure the work gets done quickly and doesn’t affect production.
- Maintenance personnel and technicians use SAP PM to improve work processes and efficiency. For example, they can review maintenance records and determine if they must undertake or plan for further maintenance activities.
- Purchasing departments can use PM to manage and execute work orders and purchase requisitions for nonstock spare parts and maintenance services.
Integration of SAP PM with other SAP modules
SAP PM integrates with many other SAP ECC components: MM, Quality Management, Production Planning, SD, FI, Controlling, Human Capital Management and Customer Services. Such integrations keep data in the module current.
These integrations ensure that any required processes for maintenance and customer service trigger automatically. This prevents unnecessary delays and ensures that there are no downstream problems, such as equipment breakdown, downtime or customer complaints. For example, when a repair activity is executed through PM, it can trigger a purchase requisition activity for nonstock materials in MM.
The role of transactional data, master data and technical objects in SAP PM
Everything in SAP PM revolves around master data, such as equipment, functional location, task lists and maintenance plans. The master data provides useful context for the other data in the system. It can also define the entities involved in business transactions, which then create transactional data.
Transactional data refers to transaction-specific information, such as its amount, date and time, confirmation and maintenance order. This information enables organizations to track the flow of goods in an industrial setting.
To set up plant maintenance with SAP PM, technical systems must be mapped and structured using technical objects. SAP PM provides three options to represent technical objects:
- Functional structuring to represent functional locations.
- Object-related structuring to represent equipment.
- Combination of functional structuring and object-related structuring to represent equipment at functional locations.
A functional location is a site where equipment undergoes technical tasks, such as preventive maintenance or repairs. A functional location consists of multiple pieces that can be installed or dismantled there. By structuring technical systems using these objects, plants can also consider the system’s process-oriented or spatial structure, which can further help with maintenance planning and execution.
With object-related structuring, technical systems get subdivided into pieces of equipment to be maintained independently. To create these objects in SAP PM, plant managers can use parameters such as equipment usage location or year of construction. Once the objects are added to SAP PM, it creates an equipment master record, which helps to streamline tasks such as maintenance, data collection and recording operating time.
With the combination approach, individual objects — i.e., pieces of equipment — are installed and dismantled at a functional location. This approach is particularly useful for conducting damage analysis because it can tell users whether repeated damage to a piece of equipment is linked to the functional location or limited to a specific object from a particular manufacturer.
Brush up on the main functional components of SAP ECC.
