Transactional marketing is a business strategy that focuses on single, point-of-sale transactions. The emphasis is on maximizing the efficiency and volume of individual sales more than developing a relationship with the buyer.
The 4 traditional elements of transactional marketing
Transactional marketing is based on the four traditional elements of marketing, commonly known as the four P’s:
- Product. Business starts with creating a product that fulfills consumer needs. Marketers analyze market research and consumer insights to develop products that align with customer preferences and demands.
- Pricing. Determining the right price for a product is crucial. Marketers seek a balance between profitability and attractiveness to consumers. Pricing strategies consider factors such as production costs, competition and perceived value.
- Placement. Establishing an efficient distribution chain is also key. Giving consumers convenient access to products means using the right channels at the right time. This could involve working with retailers and wholesalers, or developing robust e-commerce capabilities. A whole sales ecosystem, often called a channel, might be part of the distribution chain.
- Promotion. Effective promotion builds a visible profile for a product and enhances its appeal to customers. Marketers employ advertising, public relations, sales promotions and other communication activities to advance the sales funnel, which involves generating awareness, creating interest and driving sales.
Historical background of transactional marketing
Transactional marketing has roots in the early days of commerce when the primary focus was on immediate sales. This approach evolved significantly with the advent of mass production and the development of advertising techniques in the 20th century. The rise of consumerism and advancements in distribution channels further entrenched the focus on individual transactions.
Key metrics for measuring transactional marketing success
To evaluate the effectiveness of transactional marketing strategies, businesses often rely on key performance indicators such as the following:
- Sales volume. The total number of units sold within a specific period.
- Revenue. The total income generated from sales.
- Conversion rate. The percentage of potential customers who complete a purchase.
- Average transaction value. The average amount spent by customers per transaction.
- Customer acquisition cost. The cost associated with acquiring a new customer.
Transactional marketing pros and cons
Before delving into the alternative approach of relationship marketing, it is helpful to explore the pros and cons of transactional marketing. Understanding those can help marketers make informed decisions when designing their marketing plans.
Pros of transactional marketing
Here are some of the advantages of transactional marketing:
- Increased efficiency. Transactional marketing focuses on maximizing the efficiency of individual sales. By streamlining processes and optimizing sales techniques, companies can improve their overall productivity and effectiveness in closing deals.
- Immediate revenue generation. The primary goal of transactional marketing is to drive immediate sales and revenue. This approach targets customers who are ready to make a purchase, making it an effective strategy for short-term revenue generation.
- Flexibility in offerings. Since transactional marketing is primarily concerned with individual sales, companies can tailor their offerings to specific customer needs at a given time. This flexibility allows for strategic pricing, promotions and product bundling, enabling businesses to cater to various customer segments and market conditions.
- Effective for transactional products. Some products or services naturally lend themselves to a transactional marketing approach. Low-cost consumables, one-time purchases and impulse-buy items often fit this strategy because customers for such things are more likely to engage in immediate transactions rather than seeking long-term relationships.
Cons of transactional marketing
Transactional marketing comes with several disadvantages that should be considered when determining if this strategy is optimal for your product or service:
- Lack of customer loyalty. Focusing on individual sales more than relationships with customers can result in a lack of customer retention and repeat business. Some customers might seek alternative options or better deals elsewhere.
- Missed opportunities for upselling or cross-selling. A transactional marketing approach will often neglect opportunities to upsell or cross-sell additional products or services to customers. This limits the potential for increasing the average transaction value and overall revenue.
- Reduced customer engagement. With their attention devoted to immediate sales, companies pursuing transactional marketing typically have minimal interaction with the customer beyond the point of sale. This lack of engagement limits the company’s ability to gather valuable customer insights and feedback for future improvements.
- Vulnerability to competition. Transactional marketing relies heavily on competitive pricing and promotions to attract customers. This can make businesses vulnerable to price wars and intense competition; customers with no loyalty can be drawn easily to competitors offering better deals.
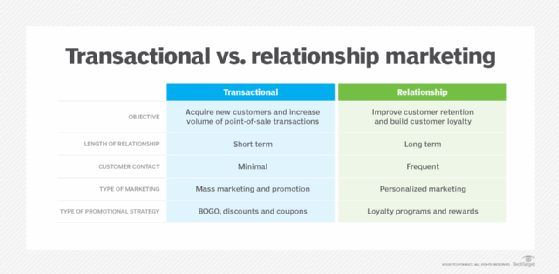
Transactional marketing has its advantages in driving immediate revenue and increasing efficiency, but it also has drawbacks in yielding little or no customer engagement. Striking a balance between transactional and relationship marketing can help businesses capitalize on short-term opportunities while building lasting customer loyalty and value.
The relationship marketing alternative
Relationship marketing prioritizes customer retention and ongoing interaction This approach aims to build long-term relationships by nurturing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Both transactional and relationship marketing approaches have their advantages and disadvantages. Transactional marketing, while highly effective in maximizing individual sales, can lead to passive, reactive and short-term customer relationships. Relationship marketing requires ongoing investment and might initially be more expensive than transactional marketing. However, it can yield higher returns on investment in the long run due to increased customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
Combining transactional and relationship marketing
Organizations often incorporate elements of both transactional and relationship marketing into their strategies. While transactional marketing might drive immediate sales and revenue, building lasting customer relationships fuels sustained success.
Employing customer relationship management (CRM) strategies can help companies foster ongoing interactions with buyers, strengthening loyalty and driving repeat business.
By integrating transactional and relationship marketing, organizations can strike a balance between short-term objectives and long-term customer value. This comprehensive approach ensures their ability to complete individual transactions efficiently without abandoning customer retention and loyalty; the combination can powerfully sustain overall business growth.
Modern trends in transactional marketing
Modern transactional marketing strategies are incorporating digital tools and technologies to enhance effectiveness. Here are some key trends:
- E-commerce platforms. Using e-commerce platforms like Shopify and Magento to streamline sales, manage inventory and process payments efficiently.
- Data analytics. Using data analytics tools like Google Analytics and Tableau to understand customer behavior and optimize marketing strategies.
- Automation. Implementing automation tools like HubSpot and Marketo for email campaigns, social media posts and targeted ads, ensuring consistent marketing efforts.
- Personalized marketing campaigns. Creating tailored marketing messages and offers using customer data to improve conversion rates.
- Real-time promotions. Launching flash sales and limited-time offers via Google Ads and Facebook Ads to drive immediate sales with a sense of urgency.
- Mobile marketing. Optimizing websites for mobile devices and using SMS marketing and mobile apps to reach customers on the go.
- Social media integration. Facilitating direct purchases from social channels with features like Instagram Shopping and Facebook Marketplace.
- Customer reviews and testimonials. Encouraging positive reviews on platforms like Yelp and Trustpilot to build credibility and drive sales.
- AI and machine learning. Utilizing AI tools like IBM Watson for predictive analytics, chatbots and personalized recommendations.
By adopting these trends, businesses can enhance their transactional marketing efforts, improve customer experiences and drive more sales.
Explore the key differences between transactional vs. relationship marketing. Check out top applications of artificial intelligence for business and top machine learning use cases and business applications.

